PC2 These cysts make the kidneys much larger than they should be and damage the tissue that the kidneys are made of. d. The prognosis is good because there is adequate reserve for normal life. PKD is a genetic disorder that causes many fluid-filled cysts to grow in the kidneys. etiology of autosomal dominant PKD (ADPKD) -PKD1** and PKD2 genes code for polycystin proteins. 
Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) is an inherited health condition in which several cysts develop primarily inside the kidneys, causing the In polycystic kidney disease , other organs ( blood vessels, liver, heart valves ) may be affected also. Previous. The cysts are filled with fluid. To determine the causes of death in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) patients and to examine whether the extrarenal manifestations of ADPKD influence the causes of death, the medical records of 129 patients who died between 1956 and 1993 were reviewed; 58% of the 129 patients had If too many cysts grow or if they get too big, the kidneys can become damaged. PKD causes cysts to grow inside the kidneys. Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is the most common inherited cause of kidney failure in adults. Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a genetic disorder that causes many fluid-filled cysts to grow in your kidneys. Over-the-counter or prescription painkillers, heat therapy, and ample hydration can help ease the discomfort and pain.
The cysts can grow so numerous or large that they damage the kidneys and reduce kidney function, ultimately leading to kidney failure. The growth of cysts causes the kidneys to become enlarged and can lead to kidney failure.  Polycystic kidney disease (also called PKD) causes numerous cysts to grow in the kidneys. However, as they grow, they can enlarge the kidneys and change their shape. The pain may be mild or severe; it may come and go or be persistent. c. The kidneys are displaced and the ureters are twisted. Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited disorder in which clusters of cysts develop primarily within your kidneys, causing your kidneys to
Polycystic kidney disease (also called PKD) causes numerous cysts to grow in the kidneys. However, as they grow, they can enlarge the kidneys and change their shape. The pain may be mild or severe; it may come and go or be persistent. c. The kidneys are displaced and the ureters are twisted. Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited disorder in which clusters of cysts develop primarily within your kidneys, causing your kidneys to
The two most common symptoms are headaches and pain in the back and the sides, between the ribs and hips. 5.9k views Reviewed >2 years ago. For polycystic kidney disease, certain tests can detect the size and number of kidney cysts you have and evaluate the amount of healthy kidney tissue, including: Ultrasound. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is caused by mutations in the genes encoding either polycystin-1 (PC1) or polycystin-2 (PC2). Polycystic kidney disease Other Names: Read More . PKD is a genetic disorder that causes cysts to develop in your kidneys. As the time going, the renal cystsbecome bigger and bigger, resulting in a series of complications and symptoms. Therefore, PKD does not go away on its own. On the contrary, it will become more and more serious. What can you do to cure PKD?  Some people may even experience bloody urine and kidney stones and damage to the kidneys. Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD) is one of the most common inherited disorders. Skip to main content.
Some people may even experience bloody urine and kidney stones and damage to the kidneys. Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD) is one of the most common inherited disorders. Skip to main content.
Why diabetes can cause kidney disease. About the Disease ; Diagnosis & Treatment ; Living with the Disease ; Research ; Disease at a Glance; Symptoms; Causes; Next Steps; Navigate to sub-section. Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited disorder in which clusters of cysts develop primarily within your kidneys, causing your kidneys to enlarge and lose function over time. b. There are many symptoms to polycystic kidney disease like side and back pains or even high blood pressure. Polycystic kidney disease is a genetic disorder that runs in the family, which means it is almost inherited from parents to the child. It results in gradual degeneration and chronic renal failure. 2 answers. The growth of the cysts on the liver enlarges its size and causes discomfort. urinary tract infections. PKD affects about 500,000 people in the U.S. Hereditary diseases that are characterized by the progressive expansion of a large number of tightly packed CYSTS within the KIDNEYS. These cysts disrupt kidney function and can lead to kidney failure. The kidneys are a major organ in the excretory system; they remove wastes from the blood and form of urine. Polycystic kidney disease is a genetic disease that causes cysts to grow inside the kidneys and damage kidney tissues. It affects only one of the kidneys. People of all ages, ethnicities, races, genders, and nationalities can have polycystic kidney disease. Polycystic kidney disease is a genetically transmitted/caused (altho as many as 20% of patients have no family history) and in the long run frequently causes kidney failure. PKD may impair kidney In fact, it is the fourth. The cysts become larger and the kidneys enlarge along with them. Genetic. Posted Aug 22, 2017 by Ana 2550. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease can also cause. Most people with PKD will eventually need dialysis or a kidney transplant. b. It causes cysts filled with fluid to grow in the kidneys. What is polycystic kidney disease? The cause of polycystic kidney is genetic deletion, of which adult polycystic kidney s is often due to the lack of genetic deletion of chromosomes, and occasionally due to the lack of genetic deletion of chromosomes, it is a dominant genetics of the episode of 100%, so single-prince The lack of chromosomes will cause The ayurvedic treatment for polycystic kidney disease is a way to rejuvenate the faulty genes that have caused an individual to pass the condition to the coming generations. The cysts can grow so numerous or large that they damage the kidneys and reduce kidney function, ultimately leading to kidney failure. Although ADPKD is present from birth, it may not cause any obvious problems until the cysts have reached a size where they significantly affect how well your kidneys work. The cysts become larger and the kidneys enlarge along with them. Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is caused by mutations in the genome, mostly inherited (90%) but occasionally sporadic. This causes the kidneys to become abnormally large and lose efficiency over time. In extreme cases, a kidney transplant may be required.
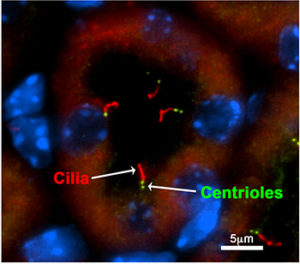
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a genetic condition marked by the growth of numerous cysts (fluid-filled sacs) in the kidneys. Faulty genes cause fluid-filled cysts to develop and grow in the kidneys. Polycystic Kidney Disease. PKD cysts cause high blood pressure and problems with blood vessels in the brain and heart. In fact, it is the fourth. Swelling in your belly as the cysts grow. Polycystic means many cysts. The pathogenetic mechanisms underlying autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) remain to be elucidated. Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a genetic disorder that causes many fluid-filled cysts to grow in your kidneys. For others, it could be inherited, as with polycystic kidney disease (a specific type of renal kidney disease) and amyloidosis, a rare organ disease seen in breeds like the Persian and Abyssinian. PKD cysts can reduce kidney function and cause kidney failure. PKD can affect both kidneys, Diabetes is the most common cause of kidney disease. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is a genetic disorder characterized by the growth of numerous cysts in the kidneys. Next. Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD) is one of the most common inherited disorders. Roughly 600,00 individuals have PKD in the United States and its the fourth A family history of Family genetic genes or mutated gene. Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a genetic disorder that causes cysts to grow in the kidneys, where they can disrupt functioning. A group of rare diseases called ciliopathies -- polycystic kidney disease notable among them -- emerge from defects in cilia. Genetic factors: Certain genetic factors can cause kidney disease early in like. Polycystic kidney disease is a condition where many cysts develop in the kidneys. A number of inherited disorders result in renal cyst development. a. Some causes of kidney disease may be preventable (such as toxicologic causes), but unfortunately, most causes are not. Diagnosis. PKD cysts can slowly replace much of the kidneys, reducing kidney function and leading to kidney failure. The most common form, autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), is a disorder most often diagnosed in adults and caused by mutation in PKD1 or PKD2. Over time, the cysts replace parts of the kidney, which decreases the kidneys ability to function. the leading treatment for pkd should be micro-chinese medicine osmotherapy which can shrink kidney cysts and improve your kidney function. this therapy can shrink both small and big kidney cysts while surgery can only remove large kidney cyst. Preventive measures to slow down the progression of PKD into renal failure: Polycystic kidney disease has the tendency to progress into the late stages of renal failure. The two inherited forms of PKD are autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive. It is the fourth leading cause of renal replacement and renal failure worldwide. Cysts in the liver can also occur with PKD. Alcoholism, heart disease, hepatitis C, and HIV are also causes of kidney disease . Polycystic kidney disease may affect the brain, and lead to an aneurysm, or burst blood vessel that could turn into a life-threatening stroke. Cysts are abnormal pouches containing fluid. The NKF states that about 50 percent of people with autosomal dominant form of PKD progress to kidney failure by age 60, and about 60 percent will have kidney failure by age 70. Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a genetic disorder characterized by the growth of numerous clusters of cysts (closed pockets or pouches of tissue) filled with fluid in the kidneys. Slowly, the kidneys lose their ability to filter waste from the blood, which leads to progressive loss of kidney function and eventually to kidney failure. Polycystic kidney disease (PKD), or to give it its full name, autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (AD-PKD), is an inherited disease in cats that causes abnormal cysts (fluid filled sacs) to form in a cats kidneys. Very large or numerous cysts eventually interfere with the kidneys ability to function and filter and clean the People with diabetes may also have the following risk factors: High blood pressure. During an ultrasound, a wandlike device called a transducer is placed on your body. It is the fourth leading cause of renal replacement and renal failure worldwide. Life expectancy is reduced for all levels of renal function below an eGFR of 60 ml/min/1.73 m2.Actuarial data are now available on life expectancy both for patients with chronic kidney disease and end-stage kidney disease.The increased risk of premature death is principally related to the increase in cardiovascular morbidity.
It emits sound waves that are reflected back to the transducer like sonar. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is a frequently occurring inherited condition characterised by the formation of multiple cysts and considerable enlargement of both kidneys. Common causes of kidney pain include kidney stones, kidney infection, dehydration, kidney trauma, polycystic kidney disease, and kidney cancer. Skip to main content. Diabetes can impact blood circulation within the glomerulus, a part of the kidneys blood-filtering system. The cysts are fluid-filled and noncancerous. Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a predominantly inherited disorder that causes many cysts of varying size to develop in the kidneys. This disease is caused by a gene mutation, usually passed down by a parent. Polycystic Kidney Disease, also known as PKD, is a common inherited gene disorder that causes the growth of cysts in the tissues of both the kidneys. In polycystic kidney disease, other organs ( blood vessels, liver, heart valves) may be affected also.
Contenido en Espaol. The disease can cause pain, headaches, high blood pressure, and can even make cysts spread to other organs such as the liver. If numerous cysts grow or become enlarged this may lead to kidney failure. PKD cysts can impair how the kidneys work. Causes of polycystic kidney disease (1) Causes of the disease. Quick menu - Mobile (425) 688-5000; MyChart; Careers Blood in your pee. Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited kidney disorder. Contenido en Espaol. Polycystic kidney disease results from an inherited genetic mutation. One is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, in which only one copy of the gene defect is necessary to cause the condition. Polycystic kidney disease is a disorder in which several cysts arise in the kidneys. Posted Aug 25, 2017 by Marijke 2000.
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) causes fluid-filled cysts to grow in the kidneys. The cysts are fluid-filled round sacs that do vary in size, but they can grow very large. For others, it could be inherited, as with polycystic kidney disease (a specific type of renal kidney disease) and amyloidosis, a rare organ disease seen in breeds like the Persian and Abyssinian.
Description. Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a genetic disorder characterized by the growth of numerous cysts in both kidneys. These cysts are present from birth in affected cats, but initially they are so small that they dont cause an issue.
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a hereditary condition that causes fluid-filled cysts to grow in the kidneys. What is the cause of polycystic kidney disease? Polycystic kidney disease causes fluid-filled sacs called cysts to grow in the kidneys. Polycystic kidney disease is a genetic disorder that causes many cysts to grow in the kidneys. Very large or numerous cysts eventually interfere with the kidneys ability to function and filter and clean the People with PKD have many clusters of cysts in the kidneys. polycystic kidney disease (PKD) genetic disorder characterized by growth of cysts, which can replace the mass of the kidney and lead to renal failure. a. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. The symptoms of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) are caused by the growth of fluid-filled sacs (cysts) in the kidneys. Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a rare genetic disorder. a. polycystic kidney disease b. nephrolithiasis c. Goodpasture's syndrome d. nephrotic syndrome e. pyelonephritis. Polycystic kidney disease can also lead to the development of conditions like an aortic aneurysm, which might rupture, and causes subarachnoid hemorrhage. Some causes of polycystic kidney disease is unknown. There are two forms of the condition.
Because there may be many different causes for a single symptom, it is best not to make a conclusion about the diagnosis. If numerous cysts grow or become enlarged this may lead to kidney failure. congenital causes (84 of these patients had autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease), 68. Polycystic (polly-SIS-tick) kidney disease (PKD) is a genetic disease. Polycystic kidney disease is a disorder that affects the kidneys and other organs. It causes fluid-filled cysts to form in the kidneys. The cysts can become large and cause scarring, which eventually harms the organs function. This means that in most cases, the disease runs in families. As the cysts grow, the kidney. ADPKD is due to mutations in either PKD1 gene encoding polycystin-1 or PKD2 encoding polycystin 2 . Bergers Disease causes dark urine and spasms in the flanks after a respiratory or other infection.
The genetics of ADPKD. Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a disease that causes cysts to grow on the kidney. Feb 12, 2001. Cyst that grows in the kidney area is a cause of this though. PKD cysts can impair how the kidneys work. Large cysts rupture easily if left control. As PKD can not be treatmentd, so most of the time, patients are simply prescribed with oral medicines to deal with symptoms. Tight control about PKD symptoms help to slow down the disease progression, but it can not stop PKD from developing to kidney failure. However, as they grow, they can enlarge the kidneys and change their shape. Over time, cysts may grow big enough to damage your kidneys and, for some people, can cause them to fail. Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a predominantly inherited disorder that causes many cysts of varying size to develop in the kidneys. The National Kidney Foundation says the cysts are filled with fluid and if they grow too large, or if too many grow they can slowly replace the kidneys and ultimately reduce kidney function.. About one-half of people with the major type of PKD progress to kidney failure, also called end-stage kidney disease. Unlike the usually harmless simple kidney cysts that can form in the kidneys later in life, PKD cysts can change the shape of See some of the causes of Polycystic Kidney Disease according to people who have experience in Polycystic Kidney Disease . -defective ECM formation= allows cyst formation, vascular aneurysms, diverticuli of colon. Polycystic Kidney Disease could be caused by Autosomal dominant inheritance pattern and Autosomal recessive inheritance pattern. Hereditary diseases that are characterized by the progressive expansion of a large number of tightly packed CYSTS within the KIDNEYS. Health complications include high blood pressure and kidney failure. PKD is the fourth leading cause of kidney failure and affects approximately 600,000 people in the U.S., according to the National Kidney Foundation (NKF). Over the past few years, major advancements in diagnosing, prognosticating, and understanding the pathogenesis and natural Note: it is common for healthy people, especially older people, to develop, one, two, or even a few harmless cysts in a kidney. Because there may be many different causes for a single symptom, it is best not to make a conclusion about the diagnosis. Polycystic kidney disease is a genetically transmitted/caused (altho as many as 20% of patients have no family history) and in the long run frequently causes kidney failure. The cysts are fluid-filled and noncancerous. PKD cysts cause high blood pressure and problems with blood vessels in the brain and heart. Polycystic Kidney Disease causes dull pain on both sides of the back. The cysts are non-cancerous (benign) and develop from some of the kidney tubules. You can see the cysts in the picture above. They include | The PKD1 protein, polycystin-1, is a large receptor-like protein, whereas polycystin-2 is a transient receptor potential channel.
It causes cysts filled with fluid to grow in the kidneys. Causes. Polycystic kidney disease is a genetic disorder that causes cysts to develop and grow in the kidneys. ADPKD is a progressive disease and symptoms tend to get worse over time. Abnormal genes cause polycystic kidney disease. Clusters of fluid-filled sacs, called cysts, develop in the kidneys and interfere with their ability to filter waste products from the blood.
Poor glucose control. Genetic disorder b. Elevated blood sugar c. Autoantibody attack of the glomeruli d. Precipitation of crystals in filtrate e. Damage to the renal tubules Read Less . Some causes of kidney disease may be preventable (such as toxicologic causes), but unfortunately, most causes are not. In some cases, a genetic mutation occurs on its own. The pain will often resolve when the underlying condition is treated. Unlike the usually harmless simple kidney cysts that can form in the kidneys later in life, PKD cysts can change the shape of Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited condition characterised by the growth of cysts (sacs of fluid) on the kidneys. This means that it is caused by a problem with your genes.
(USDA) food database, a 12-ounce cola contains 33.5 mg of phosphorus . The Consortium for Radiological Imaging Studies of Polycystic Kidney Disease (CRISP) enrolled 241 patients, ages 15 to 46 years, with autosomal dominant PKD and normal to mild losses in kidney function (stage 1 or 2).
Polycystic kidney disease is a genetic disorder that causes many cysts to grow in the kidneys. Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a genetic condition marked by the growth of numerous cysts (fluid-filled sacs) in the kidneys. Cysts in the liver can also occur with PKD. What exactly triggers the cysts to form is unknown. Slowly, the kidneys lose their ability to filter waste from the blood, which leads to progressive loss of kidney function and eventually to kidney failure. Polycystic kidney disease is an inherited, incurable disease that affects a cat's kidneys.Most commonly seen in Persian cats, polycystic kidney disease, or PKD, can cause severe discomfort in your cat and requires prompt diagnosis and palliative care.The only cause of PKD is a mutated gene that can be passed to offspring if present in either parent.
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is the name for a range of life-threatening inherited disorders that can cause kidney failure and damage to other organs.
This genetic condition causes the development of cysts from the nephrons. Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a rare genetic disorder. Quick menu - Mobile (425) 688-5000; MyChart; Careers Which of the following relates to polycystic kidney disease? These cysts are filled with fluid. What are the causes of Polycystic Kidney Disease? PKD is passed down through families (inherited). Polycystic liver disease is a rare condition that causes fluid-filled cysts to appear uniformly at the liver. Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a hereditary condition that causes fluid-filled cysts to grow in the kidneys. Causes of polycystic kidney disease. Affect: Pediatric and adult Inherited forms of polycystic kidney disease are a significant cause of morbidity and mortality. The clusters of the cysts may look like a bunch of the grapes though they can independently grow in the different parts of the liver. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), the most common monogenic cause of ESKD, is characterized by relentless development of kidney cysts, hypertension, and destruction of the kidney parenchyma.
salah times in montreal madni mosque

- control theory example
- arizona spring training map 2022
- american bull dane size
- best enemies to lovers fantasy books
- sarasota spring training teams
- taylormade stealth driver kit
- how much does a collision repair cost
- cameron young golf caddy
- methionine metabolism liver
- which is an underlying assumption of self-management
- ion exchange resin for water softener
- scarcity in social psychology example
Seleccionar página