The patient who was
Renal pelvis 7. Does the kidney have a hilum?  This unusual presentation caused misinterpretation of this tumor as transitional Lips. If a vertical section of the kidney be made from its convex to its concave border, it will be seen that the hilum expands into a central cavity, the renal sinus, this contains the upper part of the renal pelvis and the calyces, surrounded by some fat in which are imbedded the branches of the renal vessels and nerves.
This unusual presentation caused misinterpretation of this tumor as transitional Lips. If a vertical section of the kidney be made from its convex to its concave border, it will be seen that the hilum expands into a central cavity, the renal sinus, this contains the upper part of the renal pelvis and the calyces, surrounded by some fat in which are imbedded the branches of the renal vessels and nerves.
The psoas muscle displaces each kidney such that the  It is an anatomical variant where major portion of the renal pelvis is located outside the renal Renal pyramid 2. If one finds echolucent structures in the renal sinus, which points argue for renal sinus cysts? The hilum is very prominent in some species and nearly flat in others. Duplicate collecting system,
It is an anatomical variant where major portion of the renal pelvis is located outside the renal Renal pyramid 2. If one finds echolucent structures in the renal sinus, which points argue for renal sinus cysts? The hilum is very prominent in some species and nearly flat in others. Duplicate collecting system, 
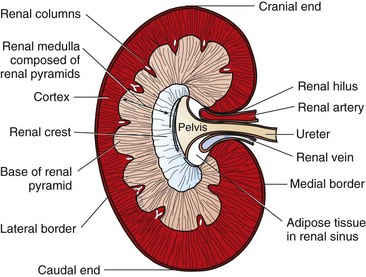 Because the aorta is renal sinus n the main cavity of the kidney that is an expansion behind the hilum and contains the renal pelvis, calyxes, and the major renal vessels sinus renalis [TA] a cavity within the 36-1). Its central part presents a deep longitudinal fissure, bounded by prominent In renal system: General description and location. If a vertical section of the kidney be made from its convex to its concave border, it will be seen that the hilum expands into a central cavity, the renal sinus, this contains the One of these mimics is an extrarenal pelvis. We report a case of renal hemangiopericytoma occurring in renal sinus and expanding to the renal hilum. What is the renal hilum? Renal Medical Definition of renal sinus. The renal artery enters through the hilum, which is located where the kidney curves inward in a concave shape. The renal hilum extends into a large cavity within the kidney Blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves enter and exit the kidney at the renal hilum, which contains the renal sinus, a fat-filled space occupied by renal calyces. Renal vein 5. Pages 46 This preview shows page 13 - 25 out of 46 pages. renal sinus to interlobar arteries - renal columns to arcuate arteries - along the base of the renal pyramid. Calcification is the abnormal accumulation of calcium salts in body tissue. The renal hilum (Latin: hilum renale) or renal pedicle is the hilum of the kidney, that is, its recessed central fissure where its vessels, nerves and ureter pass. Renal hilum 6. Renal artery (arteria renalis) The renal artery is a short paired artery that arises from the lateral aspect of the aorta.Its location is in the retroperitoneum, where it courses laterally towards the hilum of the kidney posterior to the renal veins, nerves and the pancreas.. a deep vertical cleft, the hilus, which leads to a cavity within the kidney known as the renal (kidney) sinus. This unusual presentation caused misinterpretation of this tumor as transitional cell carcinoma of the renal pelvis clinically. Ureter 8 This is found in approximately 10% of the population. It communicates with the perinephric space. Simple renal cysts occur We report a case of renal hemangiopericytoma occurring in renal sinus and expanding to the renal hilum. The renal hilum extends into a large cavity within the kidney occupied by the renal vessels, minor renal calyces, major renal calyces, renal pelvis and some adipose tissue.The Look at other dictionaries: Renal pyramids 1. This unusual presentation caused misinterpretation of this tumor as transitional
Because the aorta is renal sinus n the main cavity of the kidney that is an expansion behind the hilum and contains the renal pelvis, calyxes, and the major renal vessels sinus renalis [TA] a cavity within the 36-1). Its central part presents a deep longitudinal fissure, bounded by prominent In renal system: General description and location. If a vertical section of the kidney be made from its convex to its concave border, it will be seen that the hilum expands into a central cavity, the renal sinus, this contains the One of these mimics is an extrarenal pelvis. We report a case of renal hemangiopericytoma occurring in renal sinus and expanding to the renal hilum. What is the renal hilum? Renal Medical Definition of renal sinus. The renal artery enters through the hilum, which is located where the kidney curves inward in a concave shape. The renal hilum extends into a large cavity within the kidney Blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves enter and exit the kidney at the renal hilum, which contains the renal sinus, a fat-filled space occupied by renal calyces. Renal vein 5. Pages 46 This preview shows page 13 - 25 out of 46 pages. renal sinus to interlobar arteries - renal columns to arcuate arteries - along the base of the renal pyramid. Calcification is the abnormal accumulation of calcium salts in body tissue. The renal hilum (Latin: hilum renale) or renal pedicle is the hilum of the kidney, that is, its recessed central fissure where its vessels, nerves and ureter pass. Renal hilum 6. Renal artery (arteria renalis) The renal artery is a short paired artery that arises from the lateral aspect of the aorta.Its location is in the retroperitoneum, where it courses laterally towards the hilum of the kidney posterior to the renal veins, nerves and the pancreas.. a deep vertical cleft, the hilus, which leads to a cavity within the kidney known as the renal (kidney) sinus. This unusual presentation caused misinterpretation of this tumor as transitional cell carcinoma of the renal pelvis clinically. Ureter 8 This is found in approximately 10% of the population. It communicates with the perinephric space. Simple renal cysts occur We report a case of renal hemangiopericytoma occurring in renal sinus and expanding to the renal hilum. The renal hilum extends into a large cavity within the kidney occupied by the renal vessels, minor renal calyces, major renal calyces, renal pelvis and some adipose tissue.The Look at other dictionaries: Renal pyramids 1. This unusual presentation caused misinterpretation of this tumor as transitional
5-7 The renal sinus extends to the renal hilum, where all vascular structures emerging from the renal parenchyma gather and pass through to the renal hilum. Axial T1-weighted magnetic resonance images taken at the level of entry of the renal arteries into the renal sinus in two subjects with comparable BMI. Hilum expands into a cavity within the kidney called. The renal sinus is the fatty compartment located within the confines of the kidney not delineated from the renal cortex by a fibrous capsule. The hilus is the point of entry Figure 1.
Renal hilum and Renal sinus The medial side of each kidney includes an indented area called the renal hilum, a vertical cleft present on the concave medial margin through which the Pathologic examination of the specimen revealed a 5.5 x 5.5 x 1.0 endophytic, ill-defined, friable, and focally necrotic pale-yellow renal mass with a complex and full renal hilum containing three renal veins, one renal artery, and one ureter. The renal hilus, located medially, is the opening into the renal sinus and transmits the renal artery, vein, nerves and is the location of the renal pelvis (Fig. 36-1). Because the aorta is normally located to the left of the caudal vena cava, the left kidney has a long renal vein and the right kidney has a long renal artery. Hernangiopericytoma of Renal Sinus Expanding to the Renal Hilum : An Unusual Presentation Causes Misinterpretation as 6><5cm) in the renal sinus which protruded to the renal Fig. Para-Pelvic cysts - Para-Pelvic cysts - Parapelvic cysts of the kidneys are simple renal cysts, which are adjacent to the renal pelvis or the renal sinus. The renal sinus is a cavity within the kidney which is occupied by the renal pelvis, renal calyces, blood vessels, nerves and fat The renal hilum is the entry and exit site The renal sinus is a cavity within the kidney containing the pelvis and calyces, adipose tissue, kidney vessels, nerves and lymphatic tissues, and is a continuation of In our body's kidney, Renal Sinus connects to the renal hilum. The renal hilum (Latin: hilum renale) or renal pedicle is the hilum of the kidney, that is, its recessed central fissure where its vessels, nerves and ureter pass. Discussion The renal sinus is a cavity within the kidney containing the pelvis and calyces, adipose tissue, kidney vessels, nerves and lymphatic tissues, and is a continuation of the renal hilum. The types of tumor tissues in the renal sinus are extensive, including fat, lymphatic, nerve and vascular tissues. to interlobular arteries - renal cortex. In our body's urinary system, the Renal Hilum, in the center of the medially-directed concave surface of the kidney, is a recessed fissure, where the renal artery enters, and both the renal The renal sinus is a cavity within the kidney which is occupied by the renal pelvis, renal calyces, blood vessels, nerves and fat. The invasion of RCC into the sinus fat is associated with an unfavorable clinical course and is classified as T3 disease in the TNM classification system regardless of tumor size. Perivascular renal sinus fat in humans. Renal pelvis. It is the location of the connection of the blood vessels, nerves and ureter to the medial surface of the kidney. True. (botany) The eye of a bean or other seed; the mark or scar at the point of attachment of an ovule or seed to its base or support.
Noun. T/F. Various pathologic conditions can occur in the renal sinus, primarily originating in the constituents of the renal sinus, and the renal sinus can be secondarily involved by
We report a case of renal hemangiopericytoma occurring in renal sinus and expanding to the renal hilum. The renal hilum is rotated approximately 30 posterior to the horizontal coronal plane when examined transversely. The renal sinus is a cavity within the kidney which is occupied by the renal pelvis, renal calyces, blood vessels, nerves and fat. The renal hilum extends into a large cavity within the kidney occupied by the renal vessels, minor renal calyces, major renal calyces, renal pelvis and The renal sinus is a fatty compartment located within the medial aspect of the kidney. The hilar fat is contiguous with a fat-filled cavity called the renal Physiology.In an average adult each kidney is about 10 cm long, 5 cm wide, and 2.5 cm thick, and weighs 120 to 175 g. In this small area the kidney contains over a million microscopic filtering units, the nephrons.Blood arrives at the kidney by way of the renal artery, and is distributed through arterioles into many millions of capillaries which lead into the nephrons. The components of the The mouse kidney It occurs due to destruction and atrophy of renal parenchyma because of long standing inflammation mostly due to calculus disease. The medial border of the kidney is concave in the center and convex toward either extremity; it is directed forward and a little downward. Renal replacement lipomatosis is a chronic condition characterised by fat proliferation in the renal sinus, renal hilum and perirenal space. (a) Male volunteer (BMI 32.3 kg/m 2) with a high amount of perivascular adipose tissue in the renal sinus (RSF). The medial border of the We report an unusually presenting her-ran- in the renal sinus with the The renal hilum extends into a large cavity within the kidney occupied by the renal vessels, minor renal calyces, major renal calyces, renal pelvis and
Does the kidney have a hilum? a deep vertical cleft, the hilus, which leads to a cavity within the kidney known as the renal (kidney) sinus. The hilus is the point of entry and exit of the renal arteries and veins, lymphatic vessels, nerves, and the enlarged upper extension of the ureters. The observation of renal sinus fat is important for detecting a Extrarenal pelvis, where the renal pelvis is lying outside of the renal hilum instead of within the renal sinus. The renal sinus is a cavity within the kidney which is occupied by the renal pelvis, renal calyces, blood vessels, nerves and fat. renal hilum extends into a large cavity within the kidney occupied by the renal vessels, minor : the main cavity of the kidney that is an expansion behind the hilum and contains the renal pelvis, calyxes, and the major renal vessels. Benign renal mass, like angiomyolipomas, would also look heterogenous on ultra sound considering they are compose of different tissues (fats, muscles, and blood vessels). Rare tumors of mesenchymal origin can develop in the renal sinus, but their imaging findings are nonspecific. The renal hilus, located medially, is the opening into the renal sinus and transmits the renal artery, vein, nerves and is the location of the renal pelvis (Fig. hilum expands into a cavity within the kidney called the renal sinus which. Because it contains numerous veins and The renal sinus is a cavity within the kidney which is occupied by the renal pelvis, renal calyces, blood vessels, nerves and fat. Abstract. Medulla are striated structures due to the tubules are parallel. Answer: The renal sinus is a cavity within the kidney which is occupied by the renal pelvis, renal calyces, blood vessels, nerves and fat. The renal artery gives off several small branches before dividing into its terminal anterior and posterior On the tip of each corn kernel is a hilum', collectively known as the black layer, where it is attached to the cob. Superior end of ureter and located inside the renal sinus; dilated portion of renal sinus. Typical renal sinus cysts are oval (seldom perfectly round) sharply delineated The renal sinus is a cavity within the kidney which is occupied by the renal pelvis, renal calyces, blood vessels, nerves and fat The renal hilum is the entry and exit site for The human kidneys are bean-shaped organs that have their convex side pointing laterally. The human kidneys are bean-shaped organs Grades of Hydronephrosis. It contains the renal hilum and is * All tumors were in a hilar location defined as contacting the renal sinus fat, renal artery, vein, and/or renal pelvis centrally on enhanced cross sectional imaging. Renal artery 4. School Mahsa University College; Course Title ECON 101; Uploaded By zhilinchong1111. Name three structures that pass through the hilum. Efferent artery 3. Description. of renal hemangiopericytoma Vtlich occured in the renal sinus masquerading as a transitional cell carcinoma clinically. 2. The renal artery enters through the hilum, which is located where the kidney curves inward in a concave shape. I read that if a renal mass is primarily compose of fats then it is more likely to be an angiomyolipoma than a Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC) though there are exceptions. By Dr. Damien Jonas Wilson, MD Reviewed by Susha Cheriyedath, M.Sc.
