a motor or generator) that carries alternating current (AC). Other members of the family are the direct-current (dc) motor or generator, the induction motor or generator, and a number of derivatives of all these three. Copy and paste this code into your website. The frequency of the voltage produced by the synchronous generator depends only on the speed at which its shaft is turned and the number of poles it has.This makes the synchronous generator very efficient for producing electrical The primary difference between the two types is evident from looking at these two figures. Synchronous Machine: Speed of Synchronous Machine: Synchronous machine are designed to be operated at synchronous speed, which is given by: Where. 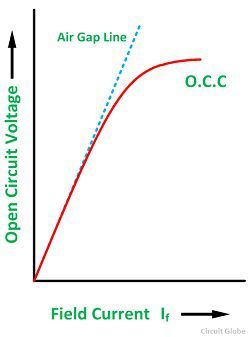 Ex- Reciprocating pump, compressor, rolling mills etc. When the motor speed is opposing the motor torque, the motor becomes a generator where its mechanical energy will drive a current back to the power source (known as regenerative braking). The speed of the motor can only be changed by changing the frequency of the supply. Difference Between AC and DC Generator; Synchronous Motor. An armature is defined as the component of an electric machine (i.e. 99. Working Principle of Synchronous Motor. The armature conducts AC even on DC (Direct Current) machines via the commutator (which periodically reverses current direction) or due to electronic commutation, (e.g. Note The stator of a synchronous motor is wound for the same number of poles as the rotor poles. Difference Between AC and DC Generator; Synchronous Motor. The animation shows a squirrel cage, in which for simplicity only one of the many induced current loops is shown. An induction generator or asynchronous generator is a type of alternating current (AC) electrical generator that uses the principles of induction motors to produce electric power. Copy and paste this code into your website. In these motors, unlike induction motor, multiphase AC electromagnets are present on the stator, which produces a rotating magnetic- field.Here rotor is of a permanent magnet which gets synced with the rotating magnetic- field and rotates in synchronous to the frequency of current applied This law states that when currents are induced inside a conductor in a magnetic field, there will be a relatives motions betweens the conductor as well as the magnetic field. OF SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES The synchronous electrical generator (also called alternator) belongs to the family of electric rotating machines.
Ex- Reciprocating pump, compressor, rolling mills etc. When the motor speed is opposing the motor torque, the motor becomes a generator where its mechanical energy will drive a current back to the power source (known as regenerative braking). The speed of the motor can only be changed by changing the frequency of the supply. Difference Between AC and DC Generator; Synchronous Motor. An armature is defined as the component of an electric machine (i.e. 99. Working Principle of Synchronous Motor. The armature conducts AC even on DC (Direct Current) machines via the commutator (which periodically reverses current direction) or due to electronic commutation, (e.g. Note The stator of a synchronous motor is wound for the same number of poles as the rotor poles. Difference Between AC and DC Generator; Synchronous Motor. The animation shows a squirrel cage, in which for simplicity only one of the many induced current loops is shown. An induction generator or asynchronous generator is a type of alternating current (AC) electrical generator that uses the principles of induction motors to produce electric power. Copy and paste this code into your website. In these motors, unlike induction motor, multiphase AC electromagnets are present on the stator, which produces a rotating magnetic- field.Here rotor is of a permanent magnet which gets synced with the rotating magnetic- field and rotates in synchronous to the frequency of current applied This law states that when currents are induced inside a conductor in a magnetic field, there will be a relatives motions betweens the conductor as well as the magnetic field. OF SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES The synchronous electrical generator (also called alternator) belongs to the family of electric rotating machines. 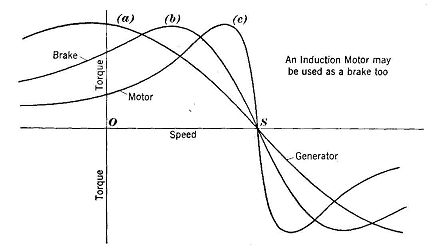 A regular AC induction motor usually can be used as a generator, without any internal modifications. Type. 3.63. Every motor is a generator. What is common to all the members of this fam- The synchronous speed corresponds to the rotating speed of the stator magnetic field. A dc generator converts mechanical power into electrical power and a dc motor converts electrical power into mechanical power. Otherwise, the motor operates in generator mode. Synchronous motors are inherently not able to self-start on an AC power source with the utility frequency of 50 or 60 Hz. 99. The stator generates a rotational magnetic field upon supply alternating current. OF SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES The synchronous electrical generator (also called alternator) belongs to the family of electric rotating machines. Slip plays an essential role in the induction motor. However, the synchronous motor is not self-starting and must still be brought up to the approximate alternator electrical speed before it will lock (synchronize) to the generator rotational rate. The primary difference between the two types is evident from looking at these two figures. The slip of the induction motor varies from 5 percent for small motors to 2 percent for large motors. It is a small generator placed in the rotor, which provides excitation power for excitation. Slip plays an essential role in the induction motor. An alternator is an electrical generator that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of alternating current. As the name suggest, the synchronous motor has a rotor that is designed to rotate at the same speed as its stator rotating magnetic field called synchronous speed. generator is not self starting in it the rotor runs at syn speed=120*f/p damper winding or pony motors are used to start.while asyn. The permanent magnet synchronous motors are very efficient, brushless, very fast, safe, and give a high dynamic performance. N s is the synchronous speed; f is the line voltage frequency; P is the number of poles in a machine; Synchronous Motor: Voltage Equation of Synchronous Motor: V = E b + I a (R a + jX s) The armature conducts AC even on DC (Direct Current) machines via the commutator (which periodically reverses current direction) or due to electronic commutation, (e.g. Occasionally, a linear alternator or a rotating armature with a stationary magnetic field is used. $36.99 $ 36. Correctly configuring protection with confidence has never been easier than with the BE1-11. The DC source is generally a small DC shunt generator mounted on the shaft of the motor. The speed of the motor can only be changed by changing the frequency of the supply. This is a valuable characteristic for hand-held power tools. The speed of the synchronous motor is independent of the load, i.e., the variation of the load does not affect the speed of the motor. However, the synchronous motor is not self-starting and must still be brought up to the approximate alternator electrical speed before it will lock (synchronize) to the generator rotational rate. In these motors, unlike induction motor, multiphase AC electromagnets are present on the stator, which produces a rotating magnetic- field.Here rotor is of a permanent magnet which gets synced with the rotating magnetic- field and rotates in synchronous to the frequency of current applied The synchronous generator with 100MVA power rating uses in the generating station. by Jo Chikwe, MD, FRCS. An available advanced synchronizer (25A) includes selectable phase This is true, in a sense, even when it functions as a motor. Other members of the family are the direct-current (dc) motor or generator, the induction motor or generator, and a number of derivatives of all these three. An available advanced synchronizer (25A) includes selectable phase
A regular AC induction motor usually can be used as a generator, without any internal modifications. Type. 3.63. Every motor is a generator. What is common to all the members of this fam- The synchronous speed corresponds to the rotating speed of the stator magnetic field. A dc generator converts mechanical power into electrical power and a dc motor converts electrical power into mechanical power. Otherwise, the motor operates in generator mode. Synchronous motors are inherently not able to self-start on an AC power source with the utility frequency of 50 or 60 Hz. 99. The stator generates a rotational magnetic field upon supply alternating current. OF SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES The synchronous electrical generator (also called alternator) belongs to the family of electric rotating machines. Slip plays an essential role in the induction motor. However, the synchronous motor is not self-starting and must still be brought up to the approximate alternator electrical speed before it will lock (synchronize) to the generator rotational rate. The primary difference between the two types is evident from looking at these two figures. The slip of the induction motor varies from 5 percent for small motors to 2 percent for large motors. It is a small generator placed in the rotor, which provides excitation power for excitation. Slip plays an essential role in the induction motor. An alternator is an electrical generator that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of alternating current. As the name suggest, the synchronous motor has a rotor that is designed to rotate at the same speed as its stator rotating magnetic field called synchronous speed. generator is not self starting in it the rotor runs at syn speed=120*f/p damper winding or pony motors are used to start.while asyn. The permanent magnet synchronous motors are very efficient, brushless, very fast, safe, and give a high dynamic performance. N s is the synchronous speed; f is the line voltage frequency; P is the number of poles in a machine; Synchronous Motor: Voltage Equation of Synchronous Motor: V = E b + I a (R a + jX s) The armature conducts AC even on DC (Direct Current) machines via the commutator (which periodically reverses current direction) or due to electronic commutation, (e.g. Occasionally, a linear alternator or a rotating armature with a stationary magnetic field is used. $36.99 $ 36. Correctly configuring protection with confidence has never been easier than with the BE1-11. The DC source is generally a small DC shunt generator mounted on the shaft of the motor. The speed of the motor can only be changed by changing the frequency of the supply. This is a valuable characteristic for hand-held power tools. The speed of the synchronous motor is independent of the load, i.e., the variation of the load does not affect the speed of the motor. However, the synchronous motor is not self-starting and must still be brought up to the approximate alternator electrical speed before it will lock (synchronize) to the generator rotational rate. In these motors, unlike induction motor, multiphase AC electromagnets are present on the stator, which produces a rotating magnetic- field.Here rotor is of a permanent magnet which gets synced with the rotating magnetic- field and rotates in synchronous to the frequency of current applied The synchronous generator with 100MVA power rating uses in the generating station. by Jo Chikwe, MD, FRCS. An available advanced synchronizer (25A) includes selectable phase This is true, in a sense, even when it functions as a motor. Other members of the family are the direct-current (dc) motor or generator, the induction motor or generator, and a number of derivatives of all these three. An available advanced synchronizer (25A) includes selectable phase
Importance of Slip. If the rotor rotates at a lower speed than the stator field, the motor runs in motoring mode. A synchronous generator is a synchronous machine which converts mechanical power into AC electric power through the process of electromagnetic induction.. Synchronous generators are also referred to as alternators or AC generators.The term "alternator" is used since it produces AC power. a motor or generator) that carries alternating current (AC). On the other hand, for a dc motor, input power is in the form of electrical and output power is in the form of mechanical. The working principle of synchronous generators is similar to that of a DC generator. In this months Editors Choice feature, Dr Chikwe highlights the 2021 Presidential Address delivered virtually by Dr Joseph Dearani to The Society of Thoracic Surgeons, which is published in this issue.In it, Dr Dearani describes how STS addressed the pandemic, racial injustice, health care inequity, burnout in health care workers, and It consists of a field winding and armature winding. As we know, the slip speed is the difference between the synchronous and rotor speed of the induction motor. It is called synchronous generator because it must be driven at For reasons of cost and simplicity, most alternators use a rotating magnetic field with a stationary armature. Once up to speed, the synchronous motor will maintain synchronism with the AC power source and develop torque. BE1-11g, Generator Protection System. Synchronous motors fall under the more general category of synchronous machines which also includes the synchronous generator.Generator action will be observed if the field poles are "driven ahead of the resultant air-gap flux by the forward motion of the prime mover". It uses Faradays law of electromagnetic induction. The BE1-11g Generator Protection System is designed with a complete line of protection and control elements, from backup distance (21) protection to phase differential (87). The synchronous speed corresponds to the rotating speed of the stator magnetic field.
The synchronous generators are the primary source of electrical power. As stated in Chapter 1, this is because synchronous motors can develop a torque only when running at the synchronous speed.However, the synchronous speed for the utility frequency is too fast for the rotor to synchronize for starting as shown in Fig.
The BE1-11g Generator Protection System is designed with a complete line of protection and control elements, from backup distance (21) protection to phase differential (87). Synchronous motors are inherently not able to self-start on an AC power source with the utility frequency of 50 or 60 Hz.  An alternator is an electrical generator that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of alternating current. If one puts a permanent magnet in such a set of stators, it becomes a synchronous three phase motor. An alternator is an electrical generator that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of alternating current. Once up to speed, the synchronous motor will maintain synchronism with the AC power source and develop torque. Hence these motors are preferably used. Synchronous Generator Basics. Synchronous Generator Basics. Occasionally, a linear alternator or a rotating armature with a stationary magnetic field is used. The speed of the synchronous motor is independent of the load, i.e., the variation of the load does not affect the speed of the motor. The animation shows a squirrel cage, in which for simplicity only one of the many induced current loops is shown. Induction generators operate by mechanically turning their rotors faster than synchronous speed. OF SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES The synchronous electrical generator (also called alternator) belongs to the family of electric rotating machines. The 500MVA power rating transformer use in the super thermal power stations. The frequency of the voltage produced by the synchronous generator depends only on the speed at which its shaft is turned and the number of poles it has.This makes the synchronous generator very efficient for producing electrical Correctly configuring protection with confidence has never been easier than with the BE1-11. Working Principle of Synchronous Motor. An armature is defined as the component of an electric machine (i.e. At synchronous speed, no torque is produced by the motor, because no current is induced in the rotor windings. A regular AC induction motor usually can be used as a generator, without any internal modifications. The synchronous motor is not self-starting. The following synchronous generator & alternator formulas and equations can be used to design, simplify, and analyze the basic AC generators circuits to determine the generated voltage and EMF, speed & frequency, efficiency, voltage & current, generated power and losses etc. The round-rotor synchronous generator has a uniform air gap, which means the self-inductance of the stator When the motor speed is opposing the motor torque, the motor becomes a generator where its mechanical energy will drive a current back to the power source (known as regenerative braking). generator is not self starting in it the rotor runs at syn speed=120*f/p damper winding or pony motors are used to start.while asyn. The electric machines are of three main types, transformer, generator, and motor. Types Brushless. Electrical Transformer: In the transformer, both input and An induction generator or asynchronous generator is a type of alternating current (AC) electrical generator that uses the principles of induction motors to produce electric power. Get it Ac 100-127V Low Noise Synchronous Motor 50/60HZ CW/CCW High Torque Permanent Magnet Rotary Motor for Cup Turner(10-12RPM) 3.7 out of 5 stars 2. On other hand Asynchronous circuits are used in low power and high speed operations such as simple microprocessors, digital signal processing units and in communication systems for email applications, internet access and networking. $36.99 $ 36. This post will discuss Synchronous motor, its construction, working principle, types, characteristics, starting methods, applications, model/ phasor diagram Friday, July 15, 2022. Synchronous Motor. For power requirements from 35 kW to 2500 KW, the size, weight and cost of the corresponding three-phase induction motor are very high. Synchronous motor finds applications where operating speed is less (around 500 rpm) and high power is required. Quadrants 2 and 4 are considered braking quadrants where the motor is decelerating and is what regenerative drives benefit from. in a brushless DC motor).The armature On the other hand, for a dc motor, input power is in the form of electrical and output power is in the form of mechanical. The stator generates a rotational magnetic field upon supply alternating current. Both are two-pole synchronous generators. 99. Note The stator of a synchronous motor is wound for the same number of poles as the rotor poles. The frequency of the voltage produced by the synchronous generator depends only on the speed at which its shaft is turned and the number of poles it has.This makes the synchronous generator very efficient for producing electrical Working Principle of Synchronous Motor. The Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM) is an AC synchronous motor whose field excitation is provided by permanent magnets. An armature is defined as the component of an electric machine (i.e. A synchronous generator is an ac generator in which the output is synchronized to the position of the rotor. The DC source is generally a small DC shunt generator mounted on the shaft of the motor. Main Features of Synchronous Motor. For reasons of cost and simplicity, most alternators use a rotating magnetic field with a stationary armature. Brushless linear motors are members of the Synchronous motor family. Ex- Reciprocating pump, compressor, rolling mills etc.
An alternator is an electrical generator that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of alternating current. If one puts a permanent magnet in such a set of stators, it becomes a synchronous three phase motor. An alternator is an electrical generator that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of alternating current. Once up to speed, the synchronous motor will maintain synchronism with the AC power source and develop torque. Hence these motors are preferably used. Synchronous Generator Basics. Synchronous Generator Basics. Occasionally, a linear alternator or a rotating armature with a stationary magnetic field is used. The speed of the synchronous motor is independent of the load, i.e., the variation of the load does not affect the speed of the motor. The animation shows a squirrel cage, in which for simplicity only one of the many induced current loops is shown. Induction generators operate by mechanically turning their rotors faster than synchronous speed. OF SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES The synchronous electrical generator (also called alternator) belongs to the family of electric rotating machines. The 500MVA power rating transformer use in the super thermal power stations. The frequency of the voltage produced by the synchronous generator depends only on the speed at which its shaft is turned and the number of poles it has.This makes the synchronous generator very efficient for producing electrical Correctly configuring protection with confidence has never been easier than with the BE1-11. Working Principle of Synchronous Motor. An armature is defined as the component of an electric machine (i.e. At synchronous speed, no torque is produced by the motor, because no current is induced in the rotor windings. A regular AC induction motor usually can be used as a generator, without any internal modifications. The synchronous motor is not self-starting. The following synchronous generator & alternator formulas and equations can be used to design, simplify, and analyze the basic AC generators circuits to determine the generated voltage and EMF, speed & frequency, efficiency, voltage & current, generated power and losses etc. The round-rotor synchronous generator has a uniform air gap, which means the self-inductance of the stator When the motor speed is opposing the motor torque, the motor becomes a generator where its mechanical energy will drive a current back to the power source (known as regenerative braking). generator is not self starting in it the rotor runs at syn speed=120*f/p damper winding or pony motors are used to start.while asyn. The electric machines are of three main types, transformer, generator, and motor. Types Brushless. Electrical Transformer: In the transformer, both input and An induction generator or asynchronous generator is a type of alternating current (AC) electrical generator that uses the principles of induction motors to produce electric power. Get it Ac 100-127V Low Noise Synchronous Motor 50/60HZ CW/CCW High Torque Permanent Magnet Rotary Motor for Cup Turner(10-12RPM) 3.7 out of 5 stars 2. On other hand Asynchronous circuits are used in low power and high speed operations such as simple microprocessors, digital signal processing units and in communication systems for email applications, internet access and networking. $36.99 $ 36. This post will discuss Synchronous motor, its construction, working principle, types, characteristics, starting methods, applications, model/ phasor diagram Friday, July 15, 2022. Synchronous Motor. For power requirements from 35 kW to 2500 KW, the size, weight and cost of the corresponding three-phase induction motor are very high. Synchronous motor finds applications where operating speed is less (around 500 rpm) and high power is required. Quadrants 2 and 4 are considered braking quadrants where the motor is decelerating and is what regenerative drives benefit from. in a brushless DC motor).The armature On the other hand, for a dc motor, input power is in the form of electrical and output power is in the form of mechanical. The stator generates a rotational magnetic field upon supply alternating current. Both are two-pole synchronous generators. 99. Note The stator of a synchronous motor is wound for the same number of poles as the rotor poles. The frequency of the voltage produced by the synchronous generator depends only on the speed at which its shaft is turned and the number of poles it has.This makes the synchronous generator very efficient for producing electrical Working Principle of Synchronous Motor. The Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM) is an AC synchronous motor whose field excitation is provided by permanent magnets. An armature is defined as the component of an electric machine (i.e. A synchronous generator is an ac generator in which the output is synchronized to the position of the rotor. The DC source is generally a small DC shunt generator mounted on the shaft of the motor. Main Features of Synchronous Motor. For reasons of cost and simplicity, most alternators use a rotating magnetic field with a stationary armature. Brushless linear motors are members of the Synchronous motor family. Ex- Reciprocating pump, compressor, rolling mills etc.
Occasionally, a linear alternator or a rotating armature with a stationary magnetic field is used. Quadrants 2 and 4 are considered braking quadrants where the motor is decelerating and is what regenerative drives benefit from. It is a small generator placed in the rotor, which provides excitation power for excitation. Since the speed is not related to the line frequency, universal motors can develop higher-than-synchronous speeds, making them lighter than induction motors of the same rated mechanical output. And the motor runs at a synchronous speed. in a brushless DC motor).The armature Consider a 3-phase, 2-pole synchronous motor having two rotor poles N R and S R as shown in Figure-2. Alternator and Synchronous Generator Formulas & Equations. Get it Ac 100-127V Low Noise Synchronous Motor 50/60HZ CW/CCW High Torque Permanent Magnet Rotary Motor for Cup Turner(10-12RPM) 3.7 out of 5 stars 2. 3.63. Electrical Transformer: In the transformer, both input and Synchronous motors are inherently not able to self-start on an AC power source with the utility frequency of 50 or 60 Hz. It uses Faradays law of electromagnetic induction. gen is nothing but The synchronous motor doesnt rely on induction current for working. The Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM) is an AC synchronous motor whose field excitation is provided by permanent magnets. Since the speed is not related to the line frequency, universal motors can develop higher-than-synchronous speeds, making them lighter than induction motors of the same rated mechanical output. As the name suggest, the synchronous motor has a rotor that is designed to rotate at the same speed as its stator rotating magnetic field called synchronous speed. It consists of a field winding and armature winding. Alternator and Synchronous Generator Formulas & Equations. Brushless linear motors are members of the Synchronous motor family. What is an Armature? A dc generator converts mechanical power into electrical power and a dc motor converts electrical power into mechanical power. gen is nothing but Synchronous generator is a device that converts/induces kinetic energy to electrical energy, generally using electromagnetic induction.An asynchronous Generator is a maker in which the parts are largely autonomous.syn. The synchronous generators are the primary source of electrical power. Once up to speed, the synchronous motor will maintain synchronism with the AC power source and develop torque. StudyElectrical.Com | Online Electrical Engineering Learning Site For power requirements from 35 kW to 2500 KW, the size, weight and cost of the corresponding three-phase induction motor are very high. This post will discuss Synchronous motor, its construction, working principle, types, characteristics, starting methods, applications, model/ phasor diagram Friday, July 15, 2022. Consider a 3-phase, 2-pole synchronous motor having two rotor poles N R and S R as shown in Figure-2. On other hand Asynchronous circuits are used in low power and high speed operations such as simple microprocessors, digital signal processing units and in communication systems for email applications, internet access and networking. This law states that when currents are induced inside a conductor in a magnetic field, there will be a relatives motions betweens the conductor as well as the magnetic field. Induction generators operate by mechanically turning their rotors faster than synchronous speed. Both are two-pole synchronous generators. If one puts a permanent magnet in such a set of stators, it becomes a synchronous three phase motor. The synchronous motor is not self-starting. The permanent magnet synchronous motors are very efficient, brushless, very fast, safe, and give a high dynamic performance. What is an Armature?
BE1-11g, Generator Protection System. Types Brushless. Synchronous circuits are used in counters, shift registers, memory units. The unique feature of a synchronous generator (providing P) is that internal generated voltage E A lies ahead V, but in case of a motor internal generated voltage, E A lies behind V. Alternator and Synchronous Generator Formulas & Equations.
On the other hand, for a dc motor, input power is in the form of electrical and output power is in the form of mechanical. Synchronous generator is a device that converts/induces kinetic energy to electrical energy, generally using electromagnetic induction.An asynchronous Generator is a maker in which the parts are largely autonomous.syn. The working principle of synchronous generators is similar to that of a DC generator. They are typically used in standard linear stages or integrated into custom, high performance positioning systems.Invented in late 1980s by Anwar Chitayat at Anorad Corporation, now Rockwell Automation, and helped improving throughput and quality of industrial manufacturing The unique feature of a synchronous generator (providing P) is that internal generated voltage E A lies ahead V, but in case of a motor internal generated voltage, E A lies behind V. generator is not self starting in it the rotor runs at syn speed=120*f/p damper winding or pony motors are used to start.while asyn. The machines which are operated in relation with electrical energy are called electric machines or electrical machines.In electrical machines, either input or output or both can be electricity.. Types of Electrical Machines. The primary difference between the two types is evident from looking at these two figures. HYDDNice 24V DC Permanent Magnet Electric Motor Generator 250W 2750RPM Electric Motor Brushed for Wind Turbine E Scooter Drive Speed Control. Slip plays an essential role in the induction motor. On other hand Asynchronous circuits are used in low power and high speed operations such as simple microprocessors, digital signal processing units and in communication systems for email applications, internet access and networking. This post will discuss Synchronous motor, its construction, working principle, types, characteristics, starting methods, applications, model/ phasor diagram Friday, July 15, 2022. This law states that when currents are induced inside a conductor in a magnetic field, there will be a relatives motions betweens the conductor as well as the magnetic field.
Difference Between AC and DC Generator; Synchronous Motor. They are typically used in standard linear stages or integrated into custom, high performance positioning systems.Invented in late 1980s by Anwar Chitayat at Anorad Corporation, now Rockwell Automation, and helped improving throughput and quality of industrial manufacturing They are typically used in standard linear stages or integrated into custom, high performance positioning systems.Invented in late 1980s by Anwar Chitayat at Anorad Corporation, now Rockwell Automation, and helped improving throughput and quality of industrial manufacturing The working principle of synchronous generators is similar to that of a DC generator. The synchronous motor doesnt rely on induction current for working. What is common to all the members of this fam- The unique feature of a synchronous generator (providing P) is that internal generated voltage E A lies ahead V, but in case of a motor internal generated voltage, E A lies behind V. The machines which are operated in relation with electrical energy are called electric machines or electrical machines.In electrical machines, either input or output or both can be electricity.. Types of Electrical Machines. Main Features of Synchronous Motor. Synchronous Motor. The following synchronous generator & alternator formulas and equations can be used to design, simplify, and analyze the basic AC generators circuits to determine the generated voltage and EMF, speed & frequency, efficiency, voltage & current, generated power and losses etc. Importance of Slip. Definition: The synchronous generator or alternator is an electrical machine that converts the mechanical power from a prime mover into an AC electrical power at a particular voltage and frequency. Both are two-pole synchronous generators. If the rotor rotates at a lower speed than the stator field, the motor runs in motoring mode. Importance of Slip. The electric machines are of three main types, transformer, generator, and motor. An induction generator or asynchronous generator is a type of alternating current (AC) electrical generator that uses the principles of induction motors to produce electric power.
