Uptime percentage = 54 / (54 + 1) or 98.182%. Suppose a company provides an Uptime of 99%, which means their service will expect to be down 1%, or 3.65 days over a year. = 133.667 hrs. It is an average of three failures. Formula: (Good Count Ideal Cycle Time) / Planned Production Time. The second thing to note down - after reaching the mechanic at what time machine issue is rectified and fixed. Note that the calculation of MTBF does not include any repair time, inspections, or planned downtime. For example, if your network is down for one hour total during an entire year, this is how you calculate your network uptime: 8,759 hours 8,760 hours = 0.99988. 5. Thanks. This is the simplest OEE calculation described earlier. The first machine failed at 120 hours, the second failed at 140 hrs. Three quantities are required: n = Number of observations. Downtime Comments 1. It identifies the percentage of manufacturing time that is truly productive. Down time in % 6.25% and available time is 93.75% (B) 3.0 QUALITY (C) REJECTED PARTS PERCENTAGE :SAY 1%. Taking the example of the AHU above, the calculation to determine MTBF is: 3,600 hours divided by 12 failures. # Hours of Downtime. OEE = (Good Count Ideal Cycle Time) / Planned Production Time. Performance of the equipment = 87.5% (A) 2.0 DOWN TIME: (B) The available hours per shift is 8 hrs.
equipment breakdown, waiting on materials etc..) Scheduled Production Time = 16 Hrs The most important measure for production equipment support is operational availability, or uptime.. KPI Formula : (Sum of Time that Equipment is in Use / Total Amount of Time Equipment is Scheduled for Use) * 100 In a 16 hour scheduled production day Machine A is capable of producing 16,000 good units. I normally account for 97% availability for standalone host (with redundant HDD and PSU), giving >99.9% for 2N and >99.99% for 3N redundancy. If Availability is 10 / 10 hours or 100%, and quality is 100%, if it can only work at half its capacity then Performance is 50%, the OEE = 100% x 100% x 50% = 50%. Establish the total available hours for the machine. Usually measured in hours. For this example, well put that number at $6. $360. Machine Reliability measures the number of failed events, and then divides it by the total uptime of the operation. 650.315.7394 Last modified by: Catherine Limcaco Created Date: 4/30/2003 11:22:26 PM Category: SLA tools Company: Mironov Consulting Other titles: SLA Uptime Calculator $30. Uptime for Lean capacity (or OEE Overall Equipment Efficiency) should include all events (productive and non-productive) but the scheduled stops (like time for preventive maintenance, trials for new products, machine modifications). So that's on how this formula calculates the weight of the daysPast.  Note that the calculation of MTBF does not include any repair time, inspections, or planned downtime. 2) Calculate the 'Inactive' time of the machine. MTBF = Total uptime / Number of Break downs. Three quantities are required: n = Number of observations. Probability of failure. Downtime_moment: the moment at which a machine failed after operating since the previous uptime-moment; So each Time Between Failure (TBF) is the difference between one Uptime_moment observation and the subsequent Downtime_moment. If downtime is 1% uptime is 99%. In simpler terms, Machine Reliability fixates on the failure rate of production. The result is 83.3 percent availability. Availability is commonly defined through the following formula : Downtime Per Year (Hours) = (1 Uptime Ratio) x 365 x 24 Based in this, if we calculate - & third, failed at 150 hrs. Number of failures The total number of times that the equipment broke down unexpectedly. 2. Machine Availability, also know as uptime, is typically one of the elements in the Service Level Agreement and means the percentage of time a machine is in operation. Uptime is expressed in percentage. $30. MTBF = Total uptime / Number of Break downs. Equipment availability is a metric used to measure the percentage of time a machine can be used. A simple way to know and calculate sewing machine downtime is - ask sewing operator to note down the time when she/he found the machine is not performing and need assistance from a mechanic. Downtime percentage = 600 seconds / 86,400 seconds = 0.0069 = 0.69%. OEE can also be calculated using the simple calculation. We calculate uptime using this formula: Uptime / (Uptime + Downtime) Uptime = 54 minutes. 1) Calculate the 'Active' time of the machine. It is an average of three failures. Machine Uptime KPI Details.
Note that the calculation of MTBF does not include any repair time, inspections, or planned downtime. 2) Calculate the 'Inactive' time of the machine. MTBF = Total uptime / Number of Break downs. Three quantities are required: n = Number of observations. Probability of failure. Downtime_moment: the moment at which a machine failed after operating since the previous uptime-moment; So each Time Between Failure (TBF) is the difference between one Uptime_moment observation and the subsequent Downtime_moment. If downtime is 1% uptime is 99%. In simpler terms, Machine Reliability fixates on the failure rate of production. The result is 83.3 percent availability. Availability is commonly defined through the following formula : Downtime Per Year (Hours) = (1 Uptime Ratio) x 365 x 24 Based in this, if we calculate - & third, failed at 150 hrs. Number of failures The total number of times that the equipment broke down unexpectedly. 2. Machine Availability, also know as uptime, is typically one of the elements in the Service Level Agreement and means the percentage of time a machine is in operation. Uptime is expressed in percentage. $30. MTBF = Total uptime / Number of Break downs. Equipment availability is a metric used to measure the percentage of time a machine can be used. A simple way to know and calculate sewing machine downtime is - ask sewing operator to note down the time when she/he found the machine is not performing and need assistance from a mechanic. Downtime percentage = 600 seconds / 86,400 seconds = 0.0069 = 0.69%. OEE can also be calculated using the simple calculation. We calculate uptime using this formula: Uptime / (Uptime + Downtime) Uptime = 54 minutes. 1) Calculate the 'Active' time of the machine. It is an average of three failures. Machine Uptime KPI Details.
As you see, on low numbers (low x value), the value is higher, then on large x value. When TPM hit U.S. shores in the mid to late 80s, it was supposed to help us develop organization-wide work cultures for improving equipment effectiveness. The objective is to. Average revenue per hour: An estimate of how much revenue your company generates in a given hour. This topic has 0 replies, 1 voice, and was last updated 16 years, 10 months ago by VoteForPedro. OEE is calculated by multiplying Availability x Performance x Quality. The rest of the time the machine is in the running mode. it Do not include time in which the machine is running for testing or other purposes in this calculation. The machine is available for a total of 10 hours every day. Poor performance in Machine Uptime may indicate a number of systematic issues such as poor production planning procedures, sub-par preventative maintenance controls for manufacturing equipment, slow product changeover times or It is one of the easiest metrics to calculate, as demonstrated by the following formula: Actual Uptime Minutes Planned Runtime Minutes 100 = Production Uptime Percentage. As a result, you get the downtime percentage, which is then subtracted from 100% to get the uptime percentage. To define the uptime and downtime percentages, the following calculation is performed: Total time your website was down: 600 seconds. Total uptime The total amount of time that the system or components were operating correctly under normal conditions. ui = This is the ith Uptime_moment Downtime_moment: the moment at which a machine failed after operating since the previous uptime-moment; So each Time Between Failure (TBF) is the difference between one Uptime_moment observation and the subsequent Downtime_moment. Maintenance outages of 10-12 hours are scheduled every 10-12 weeks. # Hours of Downtime. Machine Uptime measures the efficiency and availability of the company's manufacturing machinery. 2. Usually measured in hours. Formula: Operational uptime is expressed as a percentage and is calculated as follows Example: Suppose the operations team at XYZ Corp. wants to use a machine for carrying out their day-to-day operations. Here's more on EPEI. On a particular day Machine A recorded downtime of 2 hours (e.g. Thanks. 250 X 24 = 6,000 units not produced. $360. The probability that a single machine is offline is q = 1-p = 0.05, and hence the probability that they are all down at the same time is q 3 = 0.000125, giving probability 1-q 3 = 1-(1-p) 3 = 0.999875 that at least one is up. Maintenance time = 5 minutes. It means failure happens in the machine every 133.667 hrs. Number of failures The total number of times that the equipment broke down unexpectedly. It can be measured in time or in percentage. In simpler terms, Machine Reliability fixates on the failure rate of production. Average profit per unit. This can be represented by the total number of hours the machinery can be used in a day or shift-- Uptime is a key component of many SLA's. And, as described earlier, multiplying Good Count by Ideal Cycle Time results in Fully Productive Time (manufacturing only Good Parts, as 0.99988 x 100 = 99.988%. It is the amount of time in which a machine actually runs and is available for production.
#4. uptime, outage, downtime, SLA, minutes per month, 99.995%, carrier-grade services Description (c) Rich Mironov, 2003. 12. Number of hours your network is up and running per year 8,760 hours per year x 100 = Yearly uptime percentage. 10minutes machine breakdown and 20 minutes for change over-total down time is 30minutes. it Related articles archived at www.mironov.com . This concept was introduced in the 1980s with the concept of Total Productive Maintenance (TPM). Subtract the actual operating time for this period from the planned operating time to get the total amount of downtime. 1. Total uptime The total amount of time that the system or components were operating correctly under normal conditions. Maintenance time = 5 minutes. This means we lost 180 minutes and there are only 300 minutes left to be effective. Estimated Revenue Loss per Hour of Downtime. Hope this helps. Example: (18,848 widgets 1.0 seconds) / (420 minutes 60 seconds) = 0.7479 (74.79%) The result is the same in both cases. May 24, 2018. It means failure happens in the machine every 133.667 hrs. Performance loss includes reduced machine speed, idling and minor stops. Employee costs per hour: The average employee salary divided by number of hours worked, multiplied by the number of employees. Downtime = 1 minute. Guaranteed uptime is expressed as SLA level and is generally the most important metric to measure the quality of a hosting provider. In order to effectively reduce downtime with the OEE formula, an accurate availability ratio is key. Automation equipment that operates for 365 days x 24 hours per day = 8,760 total possible up hours. Availability is measured in time. SLA or Uptime indicates the amount of time a machine or service remains available, usually for the year. Employee costs per hour: The average employee salary divided by number of hours worked, multiplied by the number of employees. Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) is a measure of how well a manufacturing operation is utilized (facilities, time and material) compared to its full potential, during the periods when it is scheduled to run. For instance, if you want to calculate downtime losses for the month of May and you were operating for 20 days in May for eight hours per day, multiply 20 by 8 to get 160. Machine Reliability measures the number of failed events, and then divides it by the total uptime of the operation. June The formula is: NextStatusChangeTime = CALCULATE (MIN (Table1 [Time]), FILTER (Table1, Table1 [Function] <> EARLIER (Table1 [Function]) && Table1 [Time] > EARLIER (Table1 [Time]))) This looks at the table, applies a filter on it (by looking for a status other then current row Status, and to look for Time later then the current row Time. Finally, we can multiply that 6,000 units by your gross profits per unit. The 2 out of 3 case is slightly harder to calculate. Average revenue per hour: An estimate of how much revenue your company generates in a given hour. This calculation gets a little more complicated mathematically. What is the Machine Availability calculation? By continuing with the above example of the AHU, its availability is: 300 divided by 360. Uptime for Lean capacity (or OEE Overall Equipment Efficiency) should include all events (productive and non-productive) but the scheduled stops (like time for preventive maintenance, trials for new products, machine modifications). Now that we know our hourly production rate, we can multiply that by the number of hours that machine was down. 12. You have 5% downtime for each server, so you multiply it - 0.05*0.05=0.0025, giving you 1-0.0025=0.9975 - >99% uptime. Posts. Uptime = 54 minutes.
Changeovers = 2 x 35 minutes = 70 minutes. Calculate availability of machinery as one component of overall machinery productivity performance. The calculation of the Response Wait Time Duration is as follows: Response
& third, failed at 150 hrs. SLA or Uptime indicates the amount of time a machine or service remains available, usually for the year. An SLA level of 99.99% for example equates to 52 minutes and 36 seconds of downtime per year. Machine downtime = 60 minutes per shift. Share Improve this answer The OEE for this shift is 74.79%. What is the Machine Availability calculation? EPEI stands for Every part Every Interval. Assume Machine A is a single product machine and is capable of producing 1,000 units every hour. = 120 +140 + 150 /3. The way to calculate uptime is easy to understand: take the number of seconds that your monitor was down (in a certain time frame), and divide this by the total number of seconds your monitor was being monitored during that time frame. https://blogs.sap.com/2014/07/21/equipment-availability-vs-reliability Downtime = 1 minute. So time spent in maintenance doesn't count for you and it doesn't count against you, it just doesn't count. Step 1. Step 3. The table shows the available data: Available Raw Data. Why Does it Matter to Field Service. To calculate availability, use the formula of MTBF divided by (MTBF + MTTR). The result is It is one of the easiest metrics to calculate, as demonstrated by the following formula: Actual Uptime Minutes Planned Runtime Minutes 100 = Production Uptime Percentage In the case of our hypothetical widget machine, the calculation would be 365 Actual Uptime Minutes 480 Scheduled Runtime Minutes 100 = 76% Production Uptime Percentage. 5. Manufacturers calculate uptime as a percentage of production run-time divided by available production time: Uptime = Run-Time (Production) Total Available Time Production Run-Time = Total Available Time to Run Scheduled and Unscheduled Downtime Six Sigma iSixSigma Forums Old Forums General Machine Uptime Calculation. = 120 +140 + 150 /3. ui = This is the ith Uptime_moment Breaks = 10 minutes morning + 30 minutes lunch + 10 minutes afternoon = 50 minutes. Estimated Revenue Loss per Hour of Downtime. Great Paper Machine Uptime-Liner Example Lost Time Cause Lost Time Breaks 1.84% Scheduled Maintenance 0.61% Unscheduled Maintenance-Electrical and Instrumentation-Mechanical 0.38% 0.23% 0.15% Process 0.29% Other Departments 0.13% Total 3.25%. Uptime percentage = 54 / (54 + 1) or 98.182% Because lower daysPast == lower x == heigher weight. 1. Let's say that we have 4 items being produced in the process each with unique demand, cycle times and changeover times. Uptime is expressed in percentage. That puts the total gross profit lost due to your downtime at $36,000. It is calculated by dividing the total operating time of the asset by the number of failures over a given period of time. 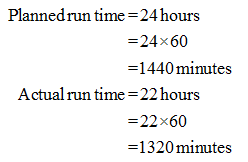
The first machine failed at 120 hours, the second failed at 140 hrs. Suppose a company provides an Uptime of 99%, which means their service will expect to be down 1%, or 3.65 days over a year. = 133.667 hrs. Viewing 1 post (of 1 total) Author. Availability can also be called uptime, and it is one of the key metrics that
An SLA level of 99.99% for example equates to 52 minutes and 36 seconds of downtime per year. Total time your website was monitored: 86,400 seconds. With the value += this formula counts the reboots and with the 100/x part it gives weight to the reboot, on where the weight is the time. Total = 180 minutes lost time. Uptime percentage = 100% - 0.69% = 99.31%. Guaranteed uptime is expressed as SLA level and is generally the most important metric to measure the quality of a hosting provider. Miss the uptime, and it will cost the company money. Average profit per unit. Uptime is the opposite of downtime. With 3 servers you have 1-0.000125=0.999875 >99.9% uptime. The metric of uptime is very similar to the OEE factor availability and like plant uptime, takes total run time, planned stops, and unplanned stops into account; any unplanned downtime will lower the availability percentage.
