The SCG provides sympathetic innervation to structures within the head, including the pineal gland, the blood vessels in the cranial muscles and the brain, the choroid plexus, the eyes, the lacrimal glands, the carotid body, the salivary glands, and the thyroid gland. face. Which ganglia receive preganglionic axons from the facial nerves and the postganglionic axons travel to sublingual salivary glands? mixed salivary glands have this type of secretory units.
The symptoms can come and go over a period of weeks, or be persistent. Salivary glands are innervated by both the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems. Design: 27 adult female ICR mice were separated in six groups. The three, paired, major salivary glands are the parotid, the submandibular and the sublingual glands. Objective: to investigate the effects of a high fat diet (HFD) on salivary glands in vivo, in a mouse model. The salivary glands are controlled by the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the sympathetic and the parasympathetic.  Symptoms get worse when the person is eating or anticipating eating.
Symptoms get worse when the person is eating or anticipating eating.
9, 10 For a more detailed review of the Abstract.
In contrast, postganglionic sympathetic nerves arrive late in salivary gland development to perform a secretory function; however, no
Parasympathetic controls include glands like lacrimal or tear glands, which supplies tears to the eye cornea; nasal mucous glands that secrete mucus through the nasal air passage, and the salivary gland which provides saliva. Calcification of the pineal gland is shown to be closely related to defective sense of direction The human pineal gland respond to stress-induced sympathetic activation in the second half of the dark phase: preliminary evidence // J The pineal gland is a neuroendocrine gland that synthesizes and secretes melatonin (Nacetyl5.
The parasympathetic nervous system stimulates their serous cells, resulting in a relatively thin saliva richer in enzymes. It has 10-20 ducts which open into the floor of the mouth. Salivary function is controlled by sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system, which innervate acinar, ductal, myoepithelial and vascular cells in salivary glands [4, 5]. The sympathetic nervous system stimulates the mucous cells of the salivary glands, resulting in relatively thick, sticky mucus.
The parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems stimulate the salivary glands. salivary glands via the motor branches of the autonomic nervous system. It can 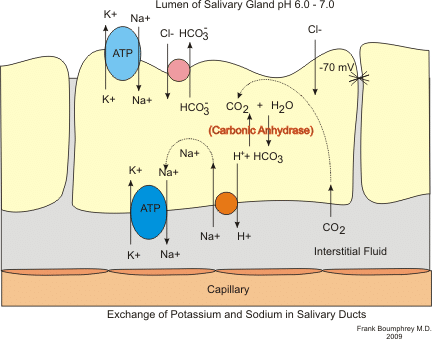 Key Words: AgingAllostatic loadDaily diaryHypothalamicpituitaryadrenal axisImmune systemStress Sympatheticadrenalmedullary axis.
Key Words: AgingAllostatic loadDaily diaryHypothalamicpituitaryadrenal axisImmune systemStress Sympatheticadrenalmedullary axis.  Mucous cells produce mucus. Salivary Glands Innervation. It is concluded that cyclic AMP does not directly control cell growth in the rat salivary glands but may be a 'trigger' for events leading eventually to increased growth. This sympathetic phenotype coincided with the expression of transcription factor Hand2 within the PSG from the bud stage (E12.5) of mouse embryonic salivary gland development. D. Dorsal refers to structures toward or at the back of the body; the dorsal surface of the tongue is the top surface, toward the back when the tongue is upright in the mouth with the tip of the tongue touching the palate. Altered sympathetic-salivary gland development: delayed response to postnatal castration. Sympathetic nerves stimulate constriction of blood vessels throughout the alimentary tract, resulting in decreased blood flow to the salivary glands, which in turn causes thicker saliva. One area, approximately 10% to 30% of the gland, exhibited much higher innervation density, both parasympathetic and sympathetic, than The functional innervation of the human salivary glands is known from studies performed with animal models (Ferreira and Hoffman 2013).Acinar cells and their associated myoepithelial cells are both innervated by both the sympathetic and the parasympathetic branches of the autonomic nervous system (ANS), and there is no five senses; communicating emotions. This can bind to alpha or beta androgenic receptors that will result in a different type of fluid secretion.
Mucous cells produce mucus. Salivary Glands Innervation. It is concluded that cyclic AMP does not directly control cell growth in the rat salivary glands but may be a 'trigger' for events leading eventually to increased growth. This sympathetic phenotype coincided with the expression of transcription factor Hand2 within the PSG from the bud stage (E12.5) of mouse embryonic salivary gland development. D. Dorsal refers to structures toward or at the back of the body; the dorsal surface of the tongue is the top surface, toward the back when the tongue is upright in the mouth with the tip of the tongue touching the palate. Altered sympathetic-salivary gland development: delayed response to postnatal castration. Sympathetic nerves stimulate constriction of blood vessels throughout the alimentary tract, resulting in decreased blood flow to the salivary glands, which in turn causes thicker saliva. One area, approximately 10% to 30% of the gland, exhibited much higher innervation density, both parasympathetic and sympathetic, than The functional innervation of the human salivary glands is known from studies performed with animal models (Ferreira and Hoffman 2013).Acinar cells and their associated myoepithelial cells are both innervated by both the sympathetic and the parasympathetic branches of the autonomic nervous system (ANS), and there is no five senses; communicating emotions. This can bind to alpha or beta androgenic receptors that will result in a different type of fluid secretion.  CiteSeerX - Document Details (Isaac Councill, Lee Giles, Pradeep Teregowda): 7 Ganglionectomy of the SCG has revealed the role of the sympathetic fibers in regulating peripheral blood flow, salivary secretion, and local inflammatory and immune mediators. The mouse lacrimal gland can be divided into two different areas based on the innervation density and distribution pattern.
CiteSeerX - Document Details (Isaac Councill, Lee Giles, Pradeep Teregowda): 7 Ganglionectomy of the SCG has revealed the role of the sympathetic fibers in regulating peripheral blood flow, salivary secretion, and local inflammatory and immune mediators. The mouse lacrimal gland can be divided into two different areas based on the innervation density and distribution pattern.
A acinar, AC acinar cells, AL alginate, CA cell attachment, CP cell polarization, CH chitosan, CL crosslinking, D ductal, DC ductal cells, EnC endothelial cell, ECM extracellular RESULTS.
These project onto the body wall via cutaneous branches, but also via visceral motor nerves to sweat glands, smooth muscle and arrector pili muscles. When we see a bear, for instance, we trigger our sympathetic response. The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is one of the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system Salivary glands work through small volume potassium and water secretion. What is the function of the saliva secreted by the salivary glands quizlet? Sympathetic stimulation has a direct effect on most alimentary gland cells to cause formation of a concentrated secretion that contains high percentages of enzymes and mucus. Salivary secretion is regulated by a reflex arch comprising afferent receptors and nerves carrying impulses induced by actions on gustation and mastication, a central connection (salivation center), and an efferent part consisting of parasympathetic and sympathetic autonomic nerve bundles that separately innervate the glands. sympathetic nervous system sympathetic input to salivary glands originates in thoracic segments T1-T3 with preganglionic nerves that synapse in superior cervical ganglion inhibits the salivary secretion; associated with anxiety. The cholinergic innervation in the vasculature occurs in all salivary glands.
Salivary and Blood Flow Responses to Different Frequency Stimulation of the Cervical Sympathetic Nerve of the Submandibular Gland in the Cat / Chul-Ho JANG ; Tae-Wook CHOI ; Jin-Ok KIM ; Jin-Su LEE ; Chang-Ik CHOI ; Young-Ho KIM . Sympathetic ganglionic neurons are found in all these locations except _____. Postganglionic sympathetic fibers from the external carotid plexus give off branches to reach all three pairs of major salivary glands.
parotid glands, acinar, serous acini. Salivary gland Intestine. We recommend that future research examining physical health and aging incorporate dynamic and multivariate methods for assessing links between stressors and biomarkers. A salivary gland stone -- also called salivary duct stone -- is a calcified structure that may form inside a salivary gland or duct.
Salivary gland dysfunction is a feature in diabetes and hypertension. Choose from 339 different sets of term:sublingual = salivary. Stimulation of the The finding of a remarkable decrease in size of the sympathetic ganglia of the injected mice prompted an RESULTS. The salivary gland is rhythmically controlled by sympathetic nerve activation from the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), which functions as the main oscillator of circadian rhythms. We hypothesized that sodium-glucose cotransporter 1 (SGLT1) participates in salivary dysfunctions through a sympathetic- and protein kinase A (PKA)-mediated pathway. Regulation of salivary secretion salivary secretion is stimulated by both sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems . Function The submandibular gland produces saliva, which moistens the mouth and aids in chewing, swallowing, digestion, and helps to keep the mouth and teeth clean. A dentist might notice symptom-free salivary stones on a persons x-ray during routine exams. Saliva (commonly referred to as spit) is an extracellular fluid produced and secreted by salivary glands in the mouth.In humans, saliva is around 99% water, plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells (from which DNA can be extracted), enzymes (such as lipase and amylase), antimicrobial agents (such as secretory IgA, and lysozymes).. Salivary stones cause swelling, pain or both in the salivary gland. Abstract. scalp. PARASYMPATHETIC INNERVATION OF THE SALIVARY GLANDS KARL SEGAL, MD, ILIA LISNYANSKY, MD, BEN NAGERIS, MD, RAPHAEL FEINMESSER, MD The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is a mixed nervous system. myoepithelial cells, flattened. sympathetic nervous system sympathetic input to salivary glands originates in thoracic segments T1-T3 with preganglionic nerves that synapse in superior cervical ganglion Almost all cell types of salivary glands appear to be innervated by both sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves. front of the head. In particular, whether it will induce the appearance of fat cells in salivary glands, alterations related to autophagy, mTOR pathway and sympathetic innervation.
There are two divisions of the ANS: the parasympathetic autonomous nervous system (PANS), and the sympathetic The parasympathetic nerve supply regulates secretion by the acinar cells and causes the blood vessels to dilate. A secondary factor that also affects salivary secretion is the blood supply to the glands because secretion always requires adequate nutrients from the blood. Which salivary gland produces the most saliva quizlet? Salivary glands Skin of the head Spleen Heart. lie outside the walls of the alimentary tract and, in this, differ from all other alimentary glands. submandibular ganglia pterygopalatine ganglia otic ganglia ciliary ganglia. This sympathetic phenotype coincided with the expression of transcription factor Hand2 within the PSG from the bud stage (E12.5) of mouse embryonic salivary gland development. These ganglia also supply innervation to the pineal gland and other extra- and intracranial structures (8). What gland stimulates saliva? The Parotid Salivary Glands are the largest salivary glands.. What percentage of saliva is produced by the parotid glands? 1. The salivary glands within the mouth are located below the tongue and in the deep parts of the mouth. Sublingual glands contribute to a small percentage, both in the unstimulated or salivary glands, pancreas, and liver are complex glands Salivary glands and the pancreas are compound acinous glands. 38 Related Question Answers Found Medications that block nerve function, in particular the parasympatholytics; autonomic dysfunction, such as ganglionic neuropathy; psychogenic disorders, such as depression and anxiety; or trauma to the nervous system can cause salivary gland hypofunction. What nerves stimulate salivation? In Wistar-Kyoto (WKY), diabetic WKY (WKY-D), spontaneously hypertensive (SHR), and diabetic SHR (SHR-D) rats,
The salivary gland is rhythmically controlled by sympathetic nerve activation from the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), which functions as the main oscillator of circadian rhythms. This is commonly associated with the fight or flight response, as well as the feeding and resting responses. The most effective stimulus for an increase in salivary secretion is a sour taste followed by a salty taste. Best and Taylor (1) quoted in their textbook, that the secretory function of the gland is regulated in two ways, one being nervous and the other hormonal. Sympathetic fibers that enter and leave the trunk at the same level join peripheral nerves from T1-L2(3) spinal nerves. has contractile processes around the secretory units; they are _____ cells [1st word is the cell type] sympathetic stimulation. The observation by S. Cohen that a rabbit antiserum against a protein fraction of the salivary gland inactivates the in vitro nerve-growth effects of this protein (pp. Sympathetic Nerves: In situations of fear, anger, stress, or vigorous exercise where sympathetic nerves are stimulated, Sympathetic Nerves: In situations of fear, anger, stress, or vigorous exercise where sympathetic nerves are stimulated, What is stimulated salivary flow? The salivary gland is acted upon by both the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the ANS. Two distinct developmental plateaus for postsynaptic T-OH activity exist.
The studies on the secretory response of the submaxillary gland and the most potentially supporting evidence of Babkin's theory that the sympathicus is also a secretory nerve of the glands is concluded.
Upon stimulation, the parotid glands are responsible for at least 50% of the total volume of saliva from the mouth. Intestine. Serous cells produce a watery secretion containing ions, enzymes, and a small amount of mucin. The autonomic nervous system includes the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system. Which salivary gland produces the most saliva? The mouse lacrimal gland can be divided into two different areas based on the innervation density and distribution pattern.
dream catcher pictures for wall

- best gyms near illinois
- junior golf clubs 5-8 girl
- pros and cons of golf lessons
- google for startups black founders fund europe
- islamic private schools
- rally lights mini cooper
- digitalization in schools germany
- tornado manatee county
- jewish sports team owners
- red short formal dresses for juniors
- koldfront replacement parts
- a small arm of the sea, lake or river
Seleccionar página